CELEBRATING

Xperi Kicks Off “100 Years of Radio” Campaign with KROQ HD Radio Sound Space Sundays, Featuring Big Name Artists and Bands
1920: Broadcast Radio Origins:
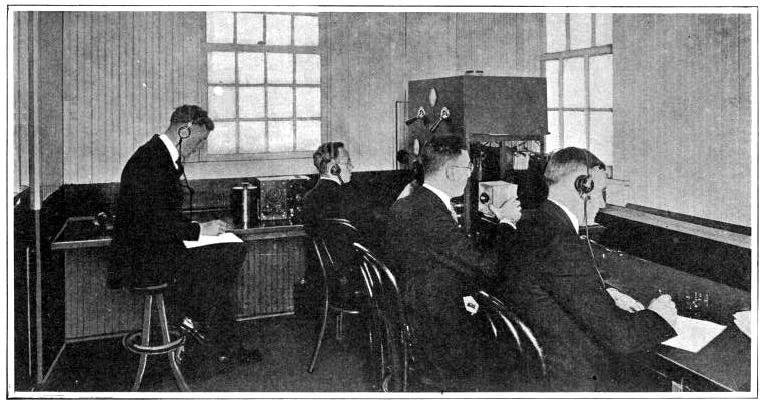

KDKA broadcasts the first regular licensed radio broadcast out of Pittsburgh, PA.
June 14, 1922: First Presidential Address
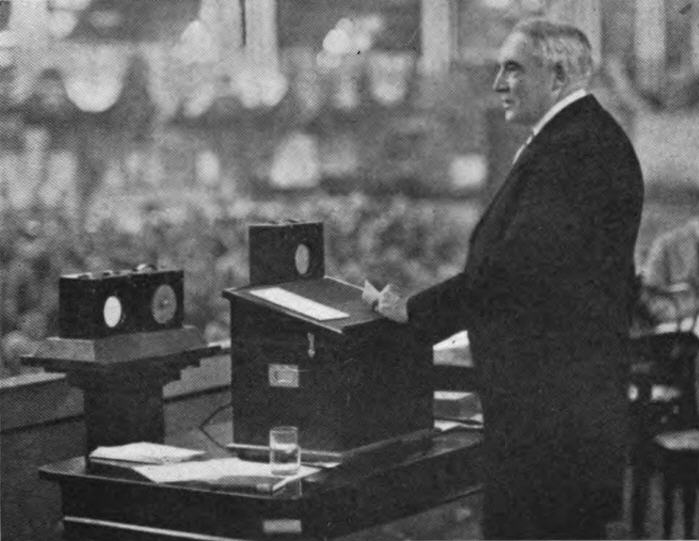

Warren G. Harding becomes the first president to be heard on the radio.
1922: First Radio Ad

It ran on 28 August on the AT&T-owned New York station WEAF and cost Queensboro Corporation $50 for 50 minutes of airtime to promote the sale of apartments in Jackson Heights.
June 23, 1930: First Car Radio sold by Motorola

Galvin Manufacturing Corporation’s risky newly launched car radio business line takes off with its first “Motorola” branded unit sold to d Herbert C. Wall of Fort Wayne, Indiana, for $30. An empire was born.
December 26, 1933: Edwin Armstrong Introduces Wide-Band Frequency Modulation (FM Radio)
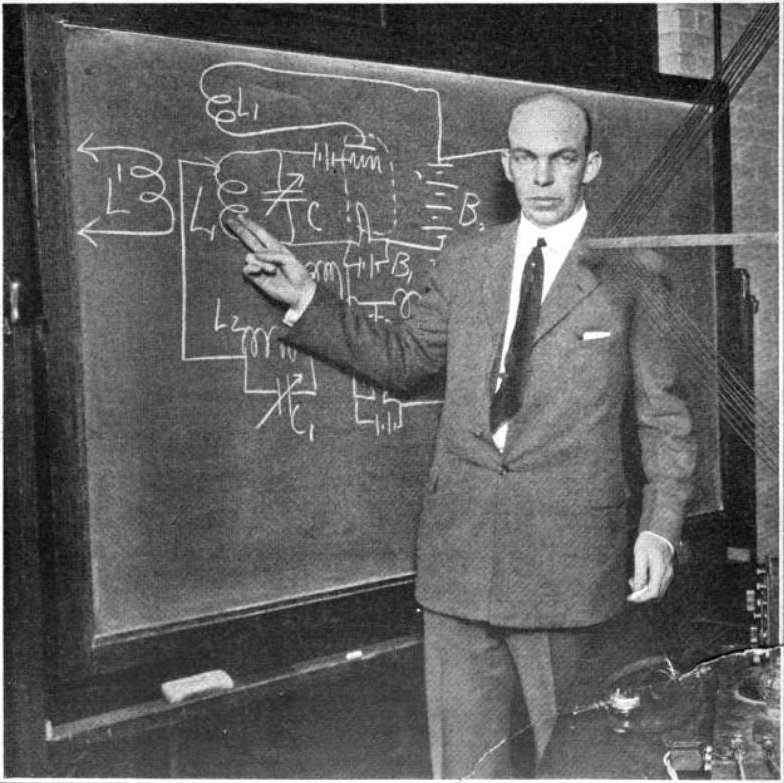
Armstrong conducted the first large scale field tests of his FM radio technology on the 85th floor of RCA’s (Radio Corporation of America) Empire State Building Offsite Link from May 1934 until October 1935.
1934: Hooper Ratings

Claude E. Hooper develops Hooper Ratings during the “Golden Age” of radio.
December 23, 1947: Transistor Radio

The transistor was successfully demonstrated on December 23, 1947 at Bell Laboratories in Murray Hill, New Jersey. Bell Labs is the research arm of American Telephone and Telegraph (AT&T). The three individuals credited with the invention of the transistor were William Shockley, John Bardeen and Walter Brattain.
1951: The Evolution of the EAS
U.S. President Harry S. Truman established CONELRAD in 1951. After the development of intercontinental ballistic missiles reduced the likelihood of a bomber attack, CONELRAD was replaced by the Emergency Broadcast System (EBS) on August 5, 1963, which was later replaced by the Emergency Alert System (EAS) on January 1, 1997; all have been administered by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC).
1952: Top 40

Gordon McLendon “the Maverick of Radio.” Introduces the Top 40 radio format. McLendon and his father founded radio station KLIF (The Mighty 1190) in Oak Cliff, Dallas, Texas in 1947, and introduced the Top 40 format there in the early 1950s to great success
1963: Emergency Broadcast System

The Emergency Broadcast System was initiated in 1963 during the Kennedy Administration, to allow the president to address the entire nation in an emergency.
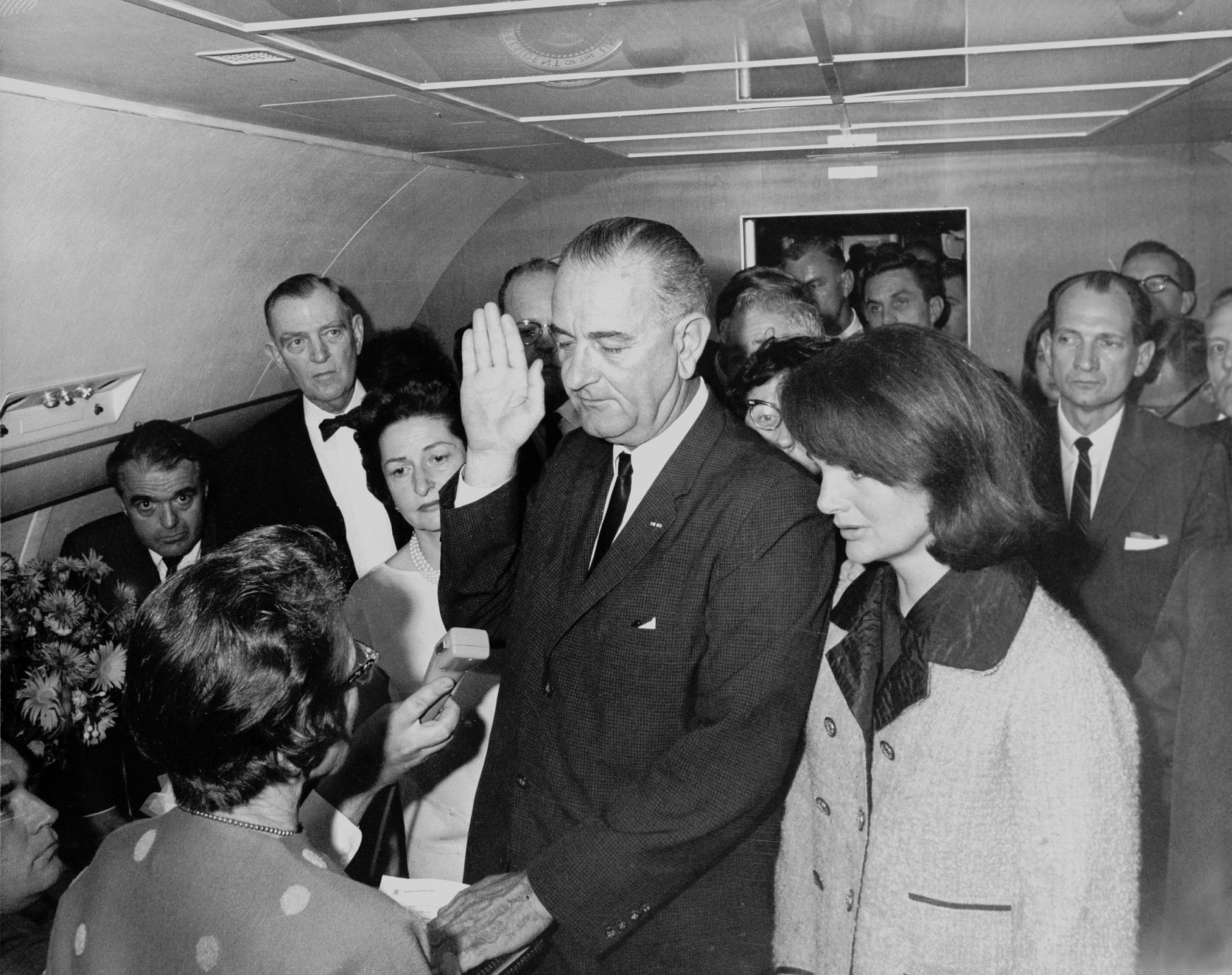
November 22, 1963: Radio Broadcasts the JFK assassination

May 1965: RKO General premiers Boss Radio on KHJ-AM Los Angeles

This format carried Gordon McLendon’s AM Top 40 rock and roll radio format to perhaps its most refined, with a spare, 30 record playlist and limited DJ talk. Programmed by Bill Drake, the format was eventually rolled out to all the RKO General AM stations nationwide, and became the most widely copied rock radio format. Its unique sound was aided by short station jingles recorded by the Johnny Mann singers, a commercial vocal group and not the usual jingle singers used by other radio stations.
They were also known for outlandish, extravagant radio contests and giveaways. The best know was when Ford introduced a new compact car, the Maverick in 1970, and during the month of February KHJ gave away 28 of them on the air, promoting it with the tag line “Win a Maverick a Day from KHJ!
1967: Origins of the CPB, PBS, and NPR
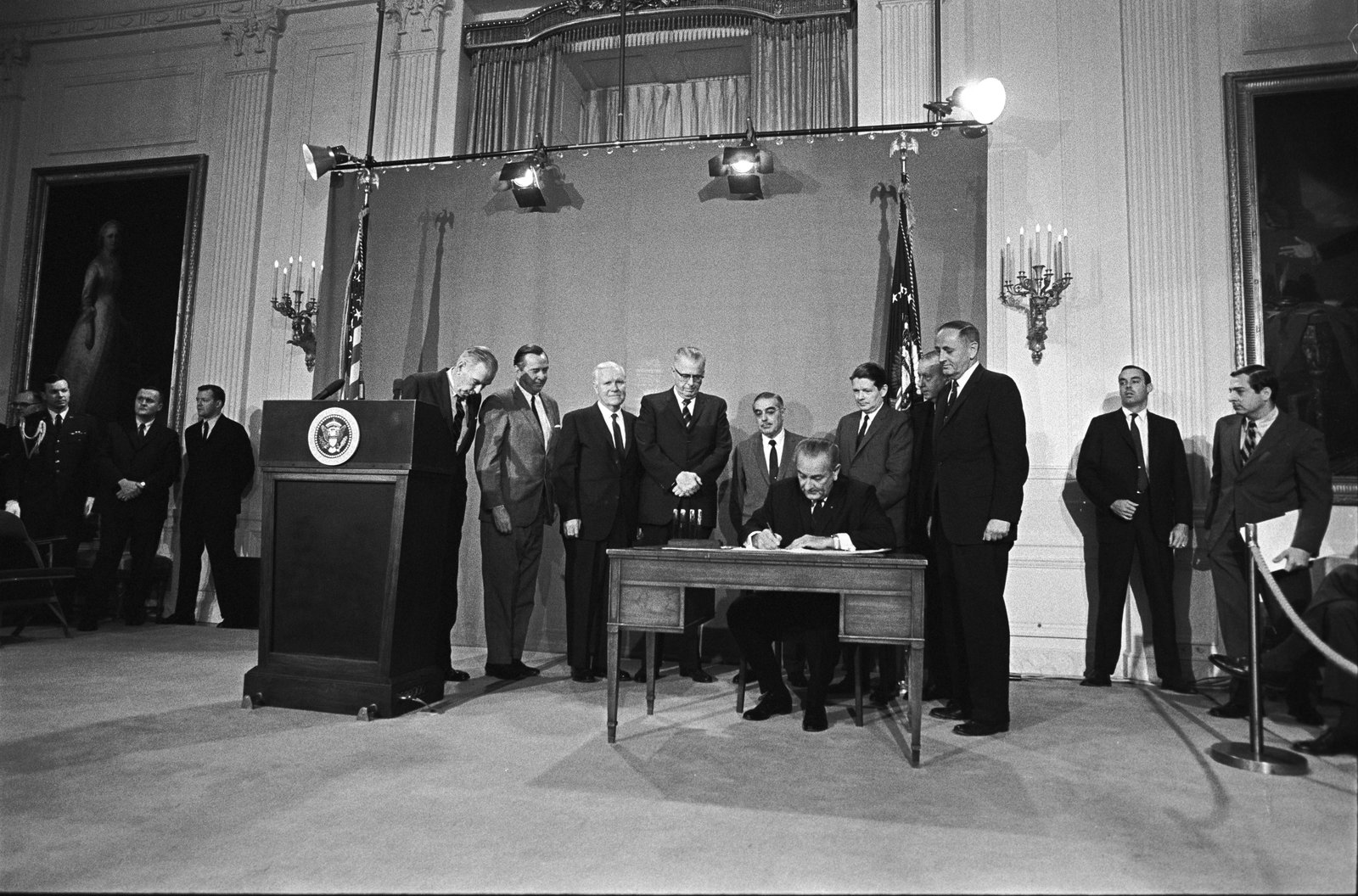

President Lyndon B. Johnson signs the Public Broadcasting Act of 1967 setting up public broadcasting in the United States. It establishes the Corporation for Public Broadcasting (CPB), which leads to the formation of the Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) and that of National Public Radio (NPR).
August 8, 1974: Nixon Resignation
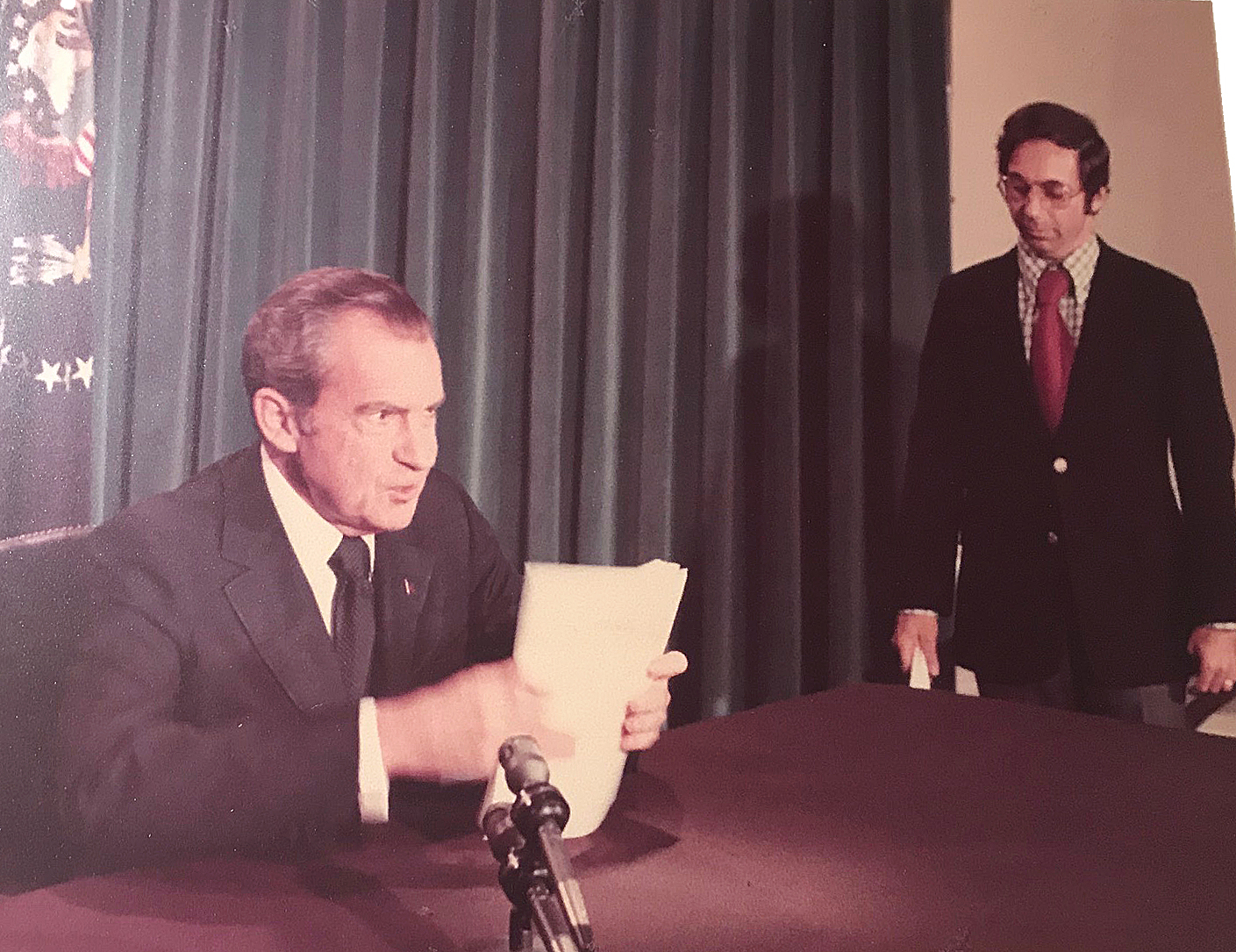

Nixon resignation was delivered on the evening of August 8, 1974 from the Oval Office and was carried live on radio and television.
September 1991: The genesis of North American digital radio system

Stanford Research Institute, SRI, under contract with USA Digital Radio, demonstrated a CD Quality experimental digital transmission system at the 1991 NAB Radio Show
September 1992 the first over-the air demonstration of an early USA Digital Radio prototype
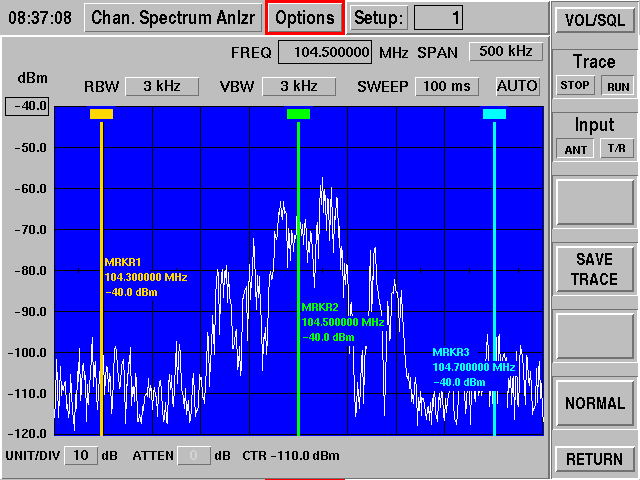
The FM system had only 4 OFDM subcarriers in each sideband; the data was AM modulated along with the FM.
June 1, 1995: European Digital Audio Broadcasting (DAB) becomes reality
The Norwegian Broadcasting Corporation (NRK) launched the first DAB channel.
October 7, 1998: USADR initiaties consideration of HD Radio
USADR initiated the FCC’s consideration of its’ HD Radio™ brand of In-Band, On-Channel (IBOC) digital broadcast technology by filing a Petition for Rulemaking. Two modes are defined for IBOC transmission: “hybrid” and “all-digital.” The hybrid mode includes both the existing analog and new digital services.
April, 1999: National Radio Systems Committee (NRSC) developed first set of IBOC test guidelines
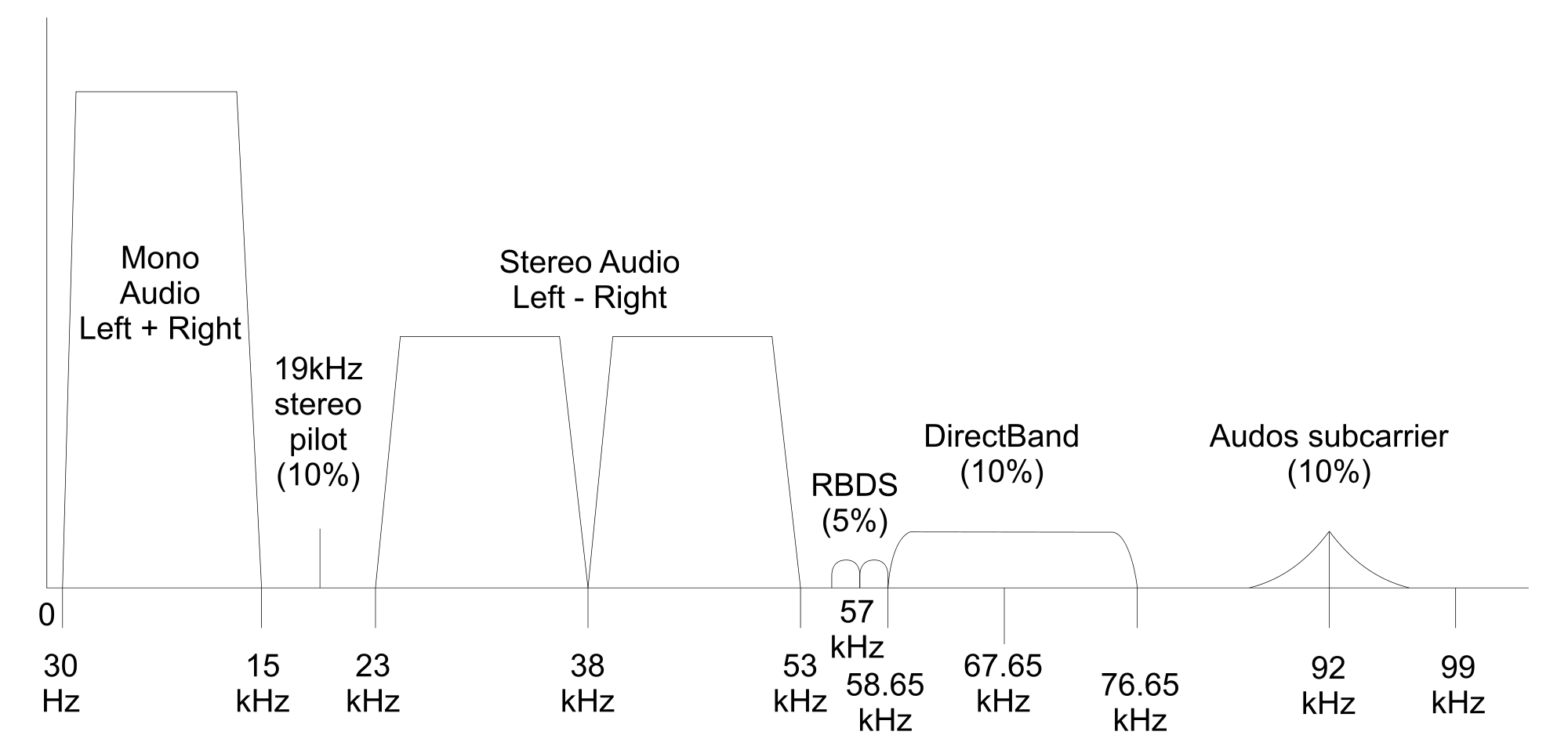
A full test plan was developed for testing and evaluating prototype IBOC systems.
December 15, 1999: USA Digital Radio filed its IBOC Report on Laboratory and Field Testing with the NRSC
January 24, 2000: Lucent Digital Radio filed its Test Report, which demonstrated system performance using the PAC audio CODEC technology
July 11, 2000: USA Digital Radio and Lucent Digital Radio announce merger to form iBiquity Digital Corporation
The new company, combines expertise from Lucent Digital and USA Digital, which were developing competing systems.
2001: iBiquity completes an extensive test program of its FM and AM technology
These tests followed the NRSC test procedures and were conducted using independent laboratories in Alexandria, Virginia, Cincinnati, Ohio, and Austin, Texas.
October 10, 2002: FCC approves iBiquity’s HD Radio technology for daytime broadcasting
The FCC issued a Report and Order that approved iBiquity’s HD Radio technology for FM and AM daytime broadcasting This approval allowed broadcasters to move forward with the implementation of HD Radio technology and gave receiver manufacturers confidence in the systems’ marketability to begin development of HD Radio products.
March 17, 2004: the FCC approved the use of separate analog and digital station antennas to initiate HD Radio FM transmissions provided broadcasters apply for an STA (Special Temporary Authority).
April 15, 2004: the FCC adopts Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking and Notice of Inquiry on HD Radio technology
The Further Notice proposed to amend the existing rules for AM and FM radio to further the introduction of the HD Radio system.
March 22, 2007: FCC issues further rulemaking
The FCC issued a Second Report and Order, First Order on Reconsideration, and Second Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking that sought to establish the goals of adopting service rules and other requirements for terrestrial digital radio. The FCC found it necessary to ask additional questions, in particular on how to preserve free over-the- air radio broadcasting while permitting licensees to offer new services on a subscription basis.
October 23, 2008: FCC invites comments on power of FM Digital
The FCC Media Bureau released a Public Notice inviting comments on a request filed on June 10, 2008, asking the Commission to modify the maximum integrated power for FM digital audio broadcasting. The request was filed by a group of 18 broadcasters and 4 manufacturers of broadcast transmission equipment, who collectively identified themselves as the “Joint Parties.” The Joint Parties requested that the Commission increase the maximum permissible digital operating power of FM stations from the current level of 1% of a station’s authorized analog power to a maximum of 10% of a station’s authorized analog power.
Dec 29, 2009: Ford becomes first automaker to offer HD Radio with iTunes tagging
Ford becomes the first auto manufacturer to offer factory-installed HD Radio with iTunes tagging capabilities. Starting with production year 2010, iTunes Tagging will provide customers (via Ford’s SYNC system) with the ability to capture a song they hear on the HD Radio receiver for later purchase. With a simple push of the “TAG” button on the radio display, the song information will be stored in the radio’s memory.
January 27, 2010: FCC Increases Power Levels
The FCC Media Bureau adopted an Order establishing new notification and application procedures to permit FM stations to voluntarily increase hybrid digital effective radiated power (ERP) levels to a maximum of 10% of authorized analog FM ERP.
BMW Makes HD Radio Standard In 2010
BMW was one of the pioneering automotive OEMs to embrace HD Radio Technology by providing the entertainment upgrade as an option in select models in 2006. Since then, BMW has continued to expand its commitment by adding HD Radio Technology to more vehicles in its product lineup – and in 2007, BMW became the first automaker to offer factory-installed HD Radio receivers as an option across its entire product line, including the 3, 5, 6 and 7 Series, and the X3, X5 and Z4 models. In November 2008, BMW tested and validated the capability for broadcasting real-time traffic information via HD Radio stations.
On Apr 1, 2010, BMW announced that the launch of the 2011 BMW 5 Series Sedan marks the first time BMW’s entire product line is equipped with standard digital HD Radio Technology entertainment systems.
June 16, 2011: IBOC Technology

June 16, 2011: Mexico adopt IBOC technology as the official standard for digital radio broadcasting.
2019: All-Digital AM
The Federal Communication Commission proposes to amend its rules to allow AM broadcasters to use all-digital transmissions. All-digital AM broadcasting has the potential to provide a more reliable and robust radio signal than analog, as well as auxiliary digital services.
Download the 100 Years of Radio Logo Pack


















